More Positive Economic Outlook
Business Cycle Tableaus by ZEW and Börsen-ZeitungEconomic Experts Remain Optimistic for Eurozone Despite Challenges
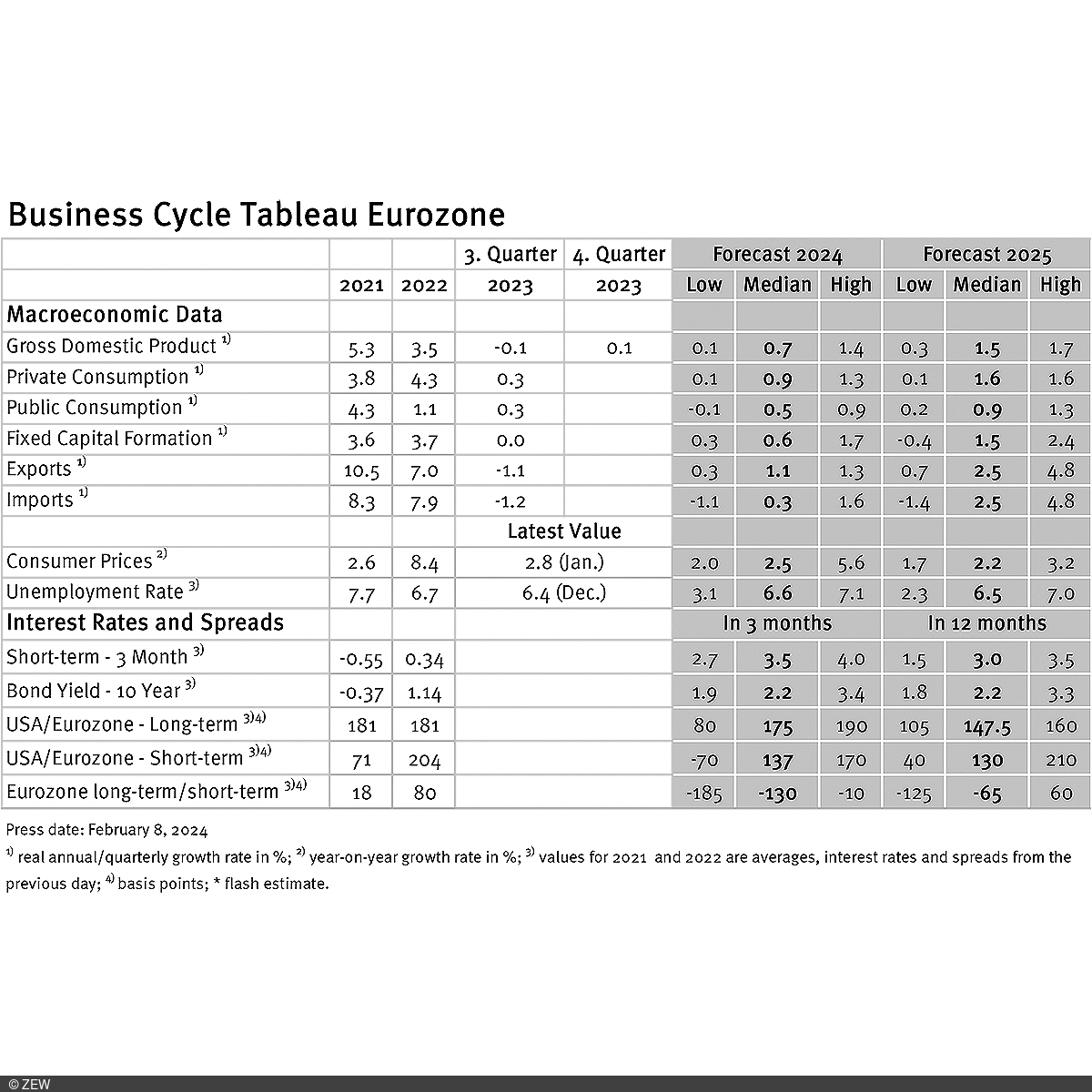
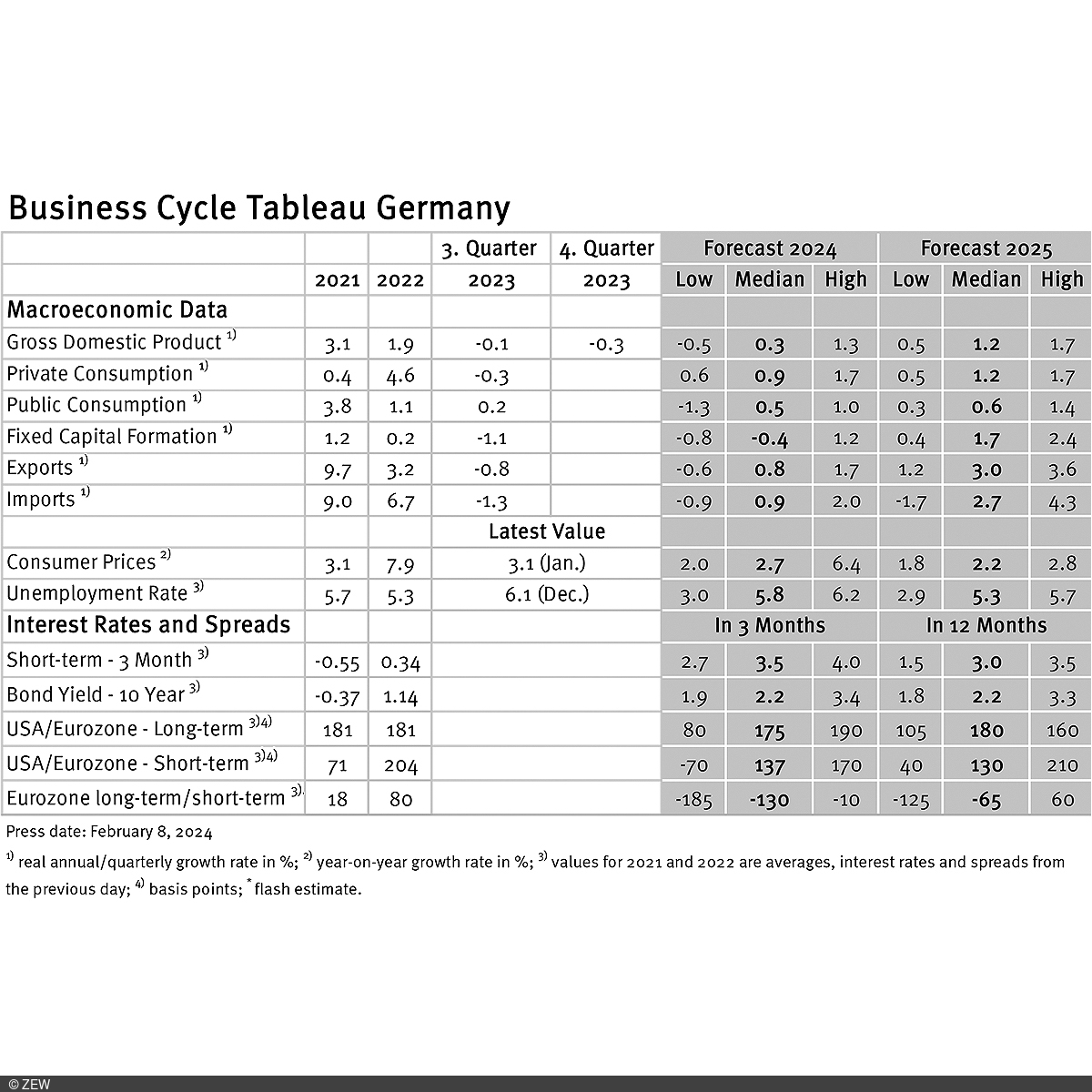
Business cycle experts are forecasting a moderately positive economic development for the eurozone in 2024, with more optimistic prospects for the coming years. Projections for Germany in 2024 are slightly more pessimistic, but follow a similar pattern. Economists are confident that despite some challenges, the long-term growth pace in both regions will be maintained, leading to overall economic stabilisation. These are the results of the business cycle tableaus by ZEW Mannheim and the German daily newspaper, Börsen-Zeitung.
The quarterly growth figures for the eurozone’s real gross domestic product (GDP) in 2023 are reported at minus 0.1 per cent for the third quarter and 0.1 per cent for the fourth quarter. For the entire year 2024, experts predict a 0.7 per cent increase in GDP, 0.1 percentage points lower than the estimate from January. Meanwhile, the range of individual growth expectations narrows from 1.7 to 1.3 percentage points, indicating a relatively high level of consensus among experts for the year 2024. A significantly stronger GDP growth of 1.5 per cent is anticipated for 2025, with an expectation range of 1.4 percentage points. The more positive outlook for 2025 is primarily driven by European foreign trade, where growth rates of 2.5 per cent are expected for both exports and imports.
Growth projections for Germany less optimistic
Quarterly growth figures for Germany in 2023 are expected to be at minus 0.1 per cent in the third quarter and at minus 0.3 per cent in the fourth quarter. Growth expectations have become somewhat more pessimistic. The experts lower their growth forecast for 2024 by 0.1 percentage points to a value of 0.3 per cent, aligning with the recent OECD forecast for Germany. Economic growth expectations for 2025 remain at 1.2 per cent. Similar to expectations for the eurozone, the projections for 2025 are thus much more optimistic than for 2024.
ECB inflation target within reach
After inflation rates in the eurozone and Germany experienced a slight increase in December 2023 following a prolonged downward trend, a decline is recorded again for January 2024. Specifically, the preliminary inflation rates stand at 2.8 per cent for the eurozone and 3.1 per cent for Germany, up 0.1 and 0.6 percentage points, respectively, from January. For the entire year 2024, inflation rates of 2.5 per cent (eurozone; unchanged from January) and 2.7 per cent (Germany; down 0.1 percentage points from January) are expected. Compared to the growth forecasts, however, the inflation expectation range with values of 3.6 (eurozone) and 4.4 (Germany) percentage points indicates significant disagreement among experts. Predicted inflation rates for the year 2025 remain unchanged at 2.2 per cent for both the eurozone and Germany, with a comparatively narrow inflation expectation range between 1.5 (eurozone) and 1.0 (Germany) percentage points. This means the majority of experts still assume that the ECB’s inflation target will be within closer reach in the coming year.
Interest rates expected to remain high in 2024 and 2025
Expectations for short-term interest rates have fallen by 0.1 percentage points to a new value of 3.5 points. At 3.0 points, the expectation for 2025 is 0.2 percentage points higher than the January value. Despite the prospect of imminent interest rate cuts by the ECB, experts continue to anticipate relatively high interest rates in the longer term. It is possible that these interest rate expectations are influenced, at least in part, by the hesitant interest rate decisions of the ECB and the Federal Reserve.
Business Cycle Tableaus by ZEW and Börsen-Zeitung
In cooperation with Börsen-Zeitung, ZEW has been publishing monthly business cycle tableaus for Germany and the eurozone with economic key figures and forecasts since 2013. Numerous banks and institutes publish reports on the current and prospective economic situation at different intervals. The information relevant for the tableau is filtered out of these publications to compute a median, minimum and maximum of the available forecasts for the current and subsequent year.
The monthly tableaus show current GDP forecasts, the expenditure breakdown, consumer prices, industrial production, unemployment rate, short- and long-term interest rates, and interest rate differentials (IDRs). The focus of the tableaus lies on national business cycle reports, which are complemented with forecasts from international banks and institutes. The tableau for the eurozone is enhanced by data from European banks and institutions.